The "Safety" Myth of East and West: Is Your Safe Haven Someone Else's Danger Zone?
.jpg)

Different cultures, environments, and lifestyles not only shape people's values but also profoundly alter our perception of public safety. For instance, in Tokyo, lightweight locks for bicycles are sufficient to prevent theft, while in New York, almost every home secures its doors tightly and prepares firearms as safety measures. Is this a cultural difference or a reflection of how Eastern and Western countries interpret safety differently?
This article explores how cultural differences between East and West shape the safety needs of various countries and influence people's daily safety precautions.
Cultural Differences Between East and West
The differences in public safety between Eastern and Western cultures reflect the profound influence of social structures and values on safety needs. From family structures to societal order, cultural differences shape how we understand and pursue "safety."
Eastern Culture: Collective Awareness and Prevention-Oriented
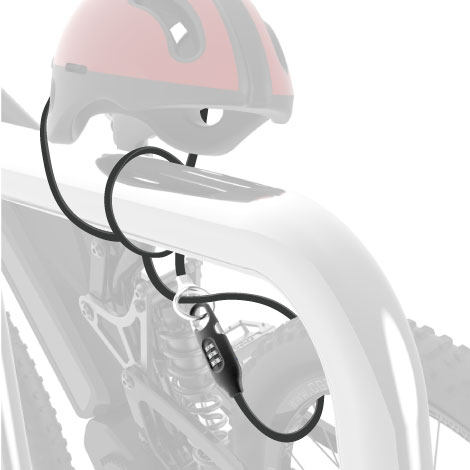
In Eastern cultures, family and societal harmony are often core values of life. This cultural background fosters a high level of collective awareness and reliance on the community. For example, Japanese society is known for its high level of order and mutual trust. Residents often trust preventive public safety measures rather than relying on excessive precaution. This cultural feature makes simple bicycle locks and other lightweight anti-theft devices widely trusted and commonly used among residents.
Western Culture: Individualism and Risk Awareness
In Western countries, especially in the United States, personal freedom and autonomy are emphasized. This cultural focus on individual risk awareness makes safety needs within families more stringent. For instance, in major cities like New York and Las Vegas, Western households often choose high-security locks or even firearms to protect themselves and their property. This heightened individual safety awareness distinguishes it from the collectivism of Eastern societies.
The Role of Geography and Social Structures in Cultural Differences
These cultural differences are closely related to geographical environments and social structures. In many Western countries (e.g., the United States and Europe), housing areas are larger, and privacy and personal space are highly valued. Consequently, security issues in these countries often focus on "how to protect property," with high trust in legal and social systems. Residents tend to rely on stringent security measures to address risks.
In contrast, Eastern countries often face limited land and high population density. This makes community and family cohesion particularly important. Residents' safety needs lean more toward public safety and community cooperation. This social structure leads to different views and approaches to personal privacy and public safety.

Trends in Lock Usage
The cultural and structural differences mentioned above are also reflected in the adoption and trends of lock usage! Below is an introduction to lock preferences in the East and West:
Eastern Countries: Simple and Practical
In densely populated regions like Japan and Taiwan, where societal cohesion is strong, simple and highly functional anti-theft devices such as bicycle locks and basic door locks are commonly chosen. These devices are designed not only to provide basic security but also to highlight a prevention-oriented cultural philosophy. In these areas, the focus of security management is often on societal collaboration and mutual trust, so residents tend to place higher trust in community safety and public facilities.
Western Countries: High-Intensity Security
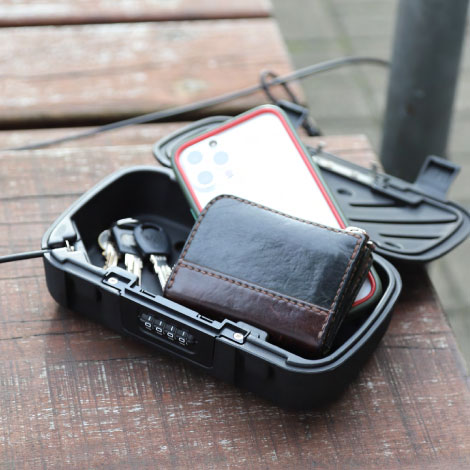
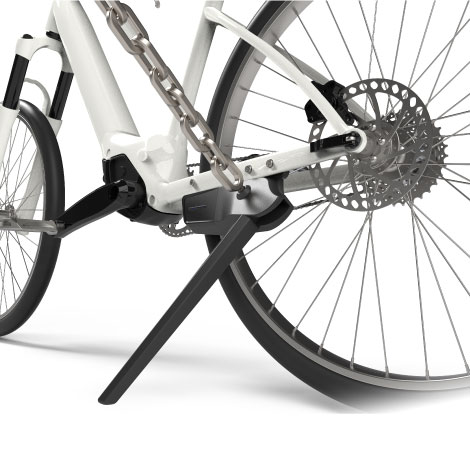
In the United States and Europe, the preference for locks reflects strong individualism and a high level of risk awareness. With larger living spaces in these countries, certain industries, such as real estate, demand high-security measures. For instance, smart locks, key storage boxes, and surveillance systems are commonly used to protect remote rental properties or homes. Additionally, due to the legalization of firearms, many American families choose gun safes to address potential security threats. These practices reflect a strong emphasis on personal defense.
According to a 2023 Statista survey, approximately 60% of American adults reported owning at least one high-security door lock or security system. In Germany, the use of smart locks has reached about 20% to 30%. In comparison, the adoption rate in Asian countries is relatively low, ranging from 5% to 10%, as most Asian consumers still prefer traditional mechanical locks. This reflects the reliance on conventional security methods in Asian cultures, as well as the lower market acceptance of smart products.
Collective Security Issues
In contrast, Eastern countries emphasize collective and community cooperation. Residents' safety often relies more on societal collaboration and regulation. For example, Singapore's community surveillance systems and patrol measures significantly reduce the need for personal protective equipment. According to Singapore police statistics, the country's crime rate has been declining year by year, demonstrating the effectiveness of its social structure and collective security model in ensuring public safety.
In summary, whether choosing traditional locks or high-tech smart locks, the choice is closely related to cultural background, social structure, and security needs.
The Importance of Localized Lock Solutions
As globalization progresses, security concerns, cultural practices, and safety requirements vary significantly across regions. It’s important to choose security measures that align with local conditions to better meet the safety needs of each area. Whether you need traditional hardware locks or cutting-edge electronic solutions, the SINOX team is committed to ensuring your security no matter where you are, providing reliable solutions for everyday challenges.
Click here to learn more







































 English
English 繁體中文
繁體中文 简体中文
简体中文